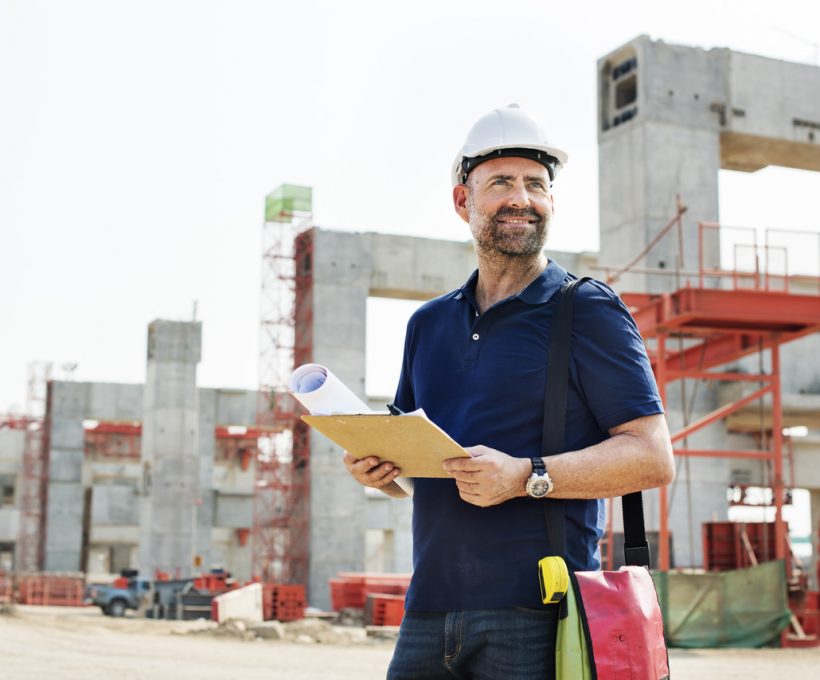
Every person working in production halls or in warehouses has encountered the definition of safety clothing at least once in their life. At least once, because this issue is raised during compulsory health and safety training, which the employer is obliged to organize periodically on the premises of the plant. But what is safety clothing actually and when should workers wear them? These are complicated issues that should be solved in the provisions of the Labor Code, because all issues related to protective clothing are regulated by Polish law and such clothing, before it is allowed for sale, must meet a number of requirements so that it is finally safe and guarantees protection for the employee. Before we move on to the detailed guidelines for occupational health and safety clothing, it is worth knowing the difference between workwear and protective clothing. Despite,that the two terms are often used interchangeably, they actually mean something completely different.
Every person working in production halls or in warehouses has encountered the definition of safety clothing at least once in their life. At least once, because this issue is raised during compulsory health and safety training, which the employer is obliged to organize periodically on the premises of the plant. But what is safety clothing actually and when should workers wear them? These are complicated issues that should be solved in the provisions of the Labor Code, because all issues related to protective clothing are regulated by Polish law and such clothing, before it is allowed for sale, must meet a number of requirements so that it is finally safe and guarantees protection for the employee. Before we move on to the detailed guidelines for occupational health and safety clothing, it is worth knowing the difference between workwear and protective clothing. Despite,that the two terms are often used interchangeably, they actually mean something completely different.
Workwear versus protective clothing
Workwear is clothing that covers or replaces the employee’s private clothing in conditions where there are no harmful factors. Workwear is adapted to the activities performed by the employee, i.e. other workwear is available to catering workers, medical services or employees of specialized laboratories.
Protective clothing is clothing that covers or replaces private clothing. Its main purpose is to protect employees against hazards that may affect their safety or health. Protective clothing should be adapted to the specific workplace, where there is a risk of injury to the body by sharp tools or penetration of harmful chemicals through the skin. Such protective clothing must have appropriate certificates that guarantee that it meets the basic safety requirements specified in the relevant standard.
Legal requirements for safety clothing
Requirements for standards that must be met by protective clothing are set out in the Labor Code. According to the provisions contained therein, occupational health and safety clothing is clothing that protects or replaces the employee’s own clothing, but it is also clothing used in specific technological, sanitary or occupational health and safety situations. Workwear used in workplaces is not subject to the compulsory certification process. So, no special labeling is required to sell it. This marking is usually special pictograms and CE markings. However, it must be made in accordance with the requirements of Polish Standards, which are specified in detail for individual types of work and places of use of such clothing.
Other provisions apply to protective clothing, which is a means of individual protection and is designed to protect the employee against the effects of factors that may occur in the workplace that are dangerous and harmful to health safety. They must therefore meet the requirements for conformity assessment. Such assessments are specified in separate regulations, and more precisely in the regulation on essential requirements for personal protective equipment.
The same regulation defines the method of dividing personal protective equipment into specific categories. The resulting requirements for the EC type examination have been assigned to each category. For example: personal protective equipment included in the group of simple design measures includes measures designed to protect against:
- the action of mechanical factors, the effects of which are superficial,
- cleaning agents that are weak and the effects of which are easily reversible,
- hazards related to working with hot objects, which does not expose the user to temperatures higher than 50 ° C or to dangerous blows,
- weather conditions, without taking into account exceptional and extremely extreme factors,
- weak blows and vibrations that do not affect important areas of life and the effects of which cannot cause irreversible damage to the body,
- sunlight.
Other standards
Depending on the type of work performed, the guidelines for occupational health and safety clothing also change. For example, if the clothing is to be resistant to metal splinters, the effects of which are mainly superficial – it is enough to use work clothes that meet the requirements of PN-P-84525: 1998 Work clothes – Work clothes (Article 2377 § 1 of the Labor Code). On the other hand, in a situation where protection against more serious than superficial effects is required, protective clothing meeting the requirements for conformity assessment (Article 2376 § 2 of the Labor Code) should be used.
The use of health and safety clothing is an obligation imposed on the employer by Polish law. Its use, however, should not only be an unpleasant obligation imposed by officials, but above all a kind of common sense. None of us want any employee to get hurt while performing their professional duties.
Sprawdź koniecznie
-
Orthopedist - what does this doctor do and what tests does he perform?
Many people have problems with the locomotor organs, sometimes they wonder which doctor to go…
-
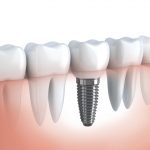
What are dental implants?
dental implantology In science to this day, there is a dispute between supporters of two…
-
What dress to go to the wedding in?
Finding the perfect dress for a wedding party is a real challenge for many women. Everyone…
-
What do I need to set up a transport company?
It cannot be denied that times are less and less certain and everyone is looking…